Zeus Survey Meter (ca. 1947-1948)
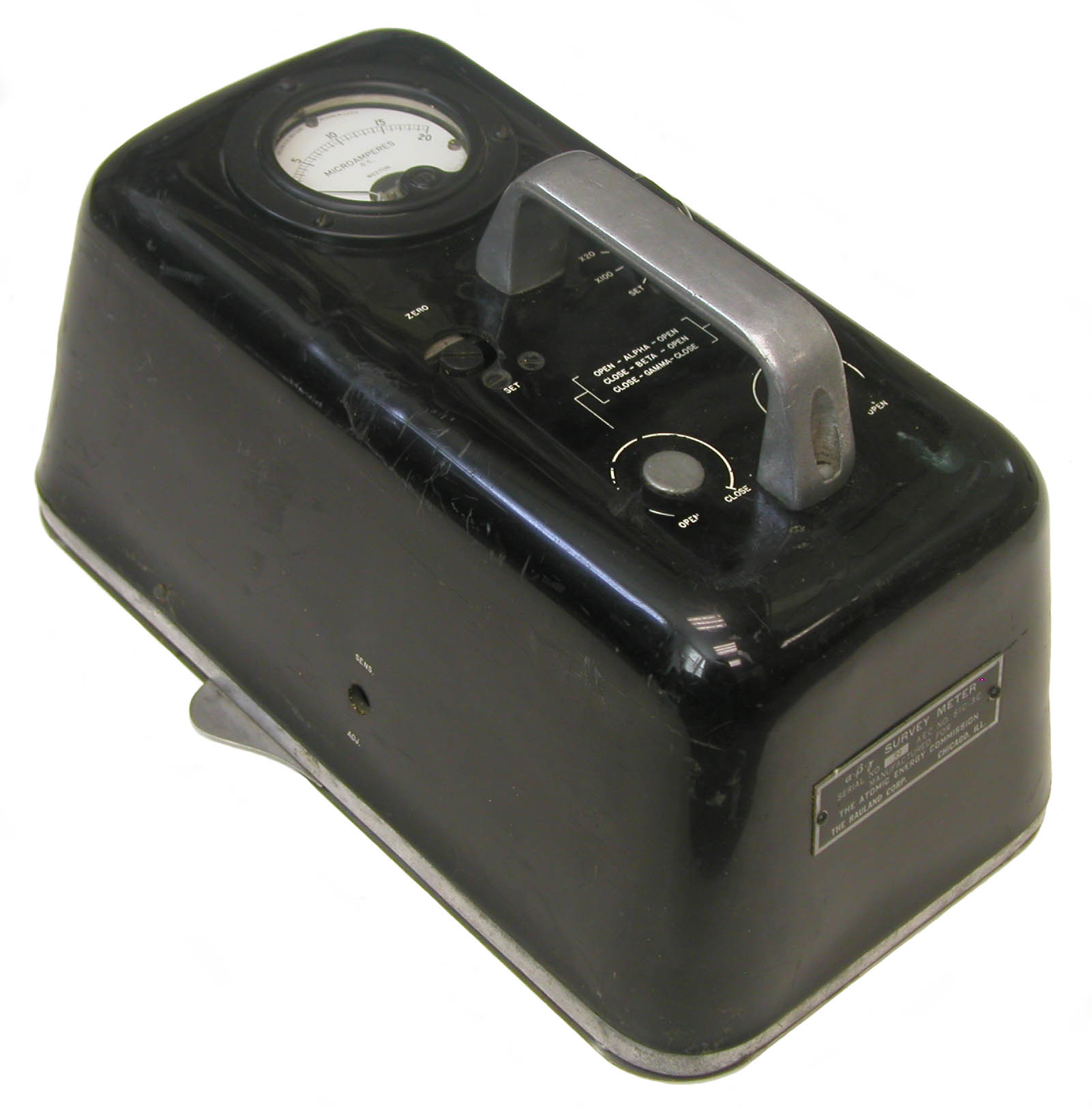

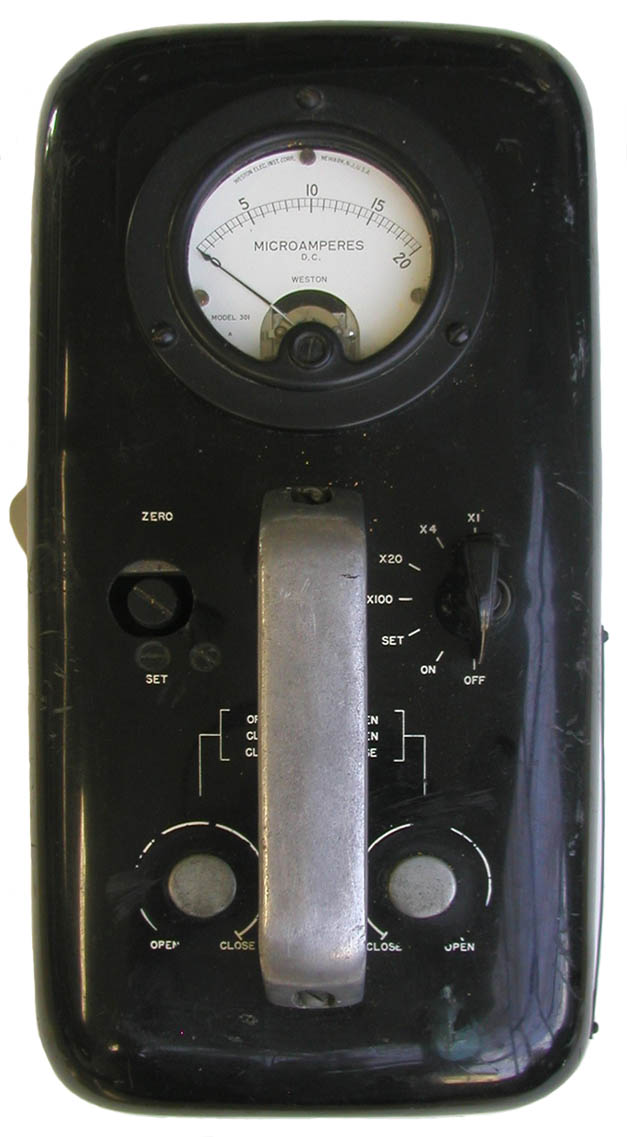
The Zeus was developed by Francis Shonka at the University of Chicago's Metallurgical Laboratory during World War II. This example was a commercial version manufactured for the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) by the Rauland Corporation. Like its descendent, the Juno, the Zeus employed an ionization chamber to measure alpha, beta and gamma radiation. The latter were distinguished by sliding thin aluminum or plastic shields over the 5 inch by 6 inch detector window (located on the bottom).
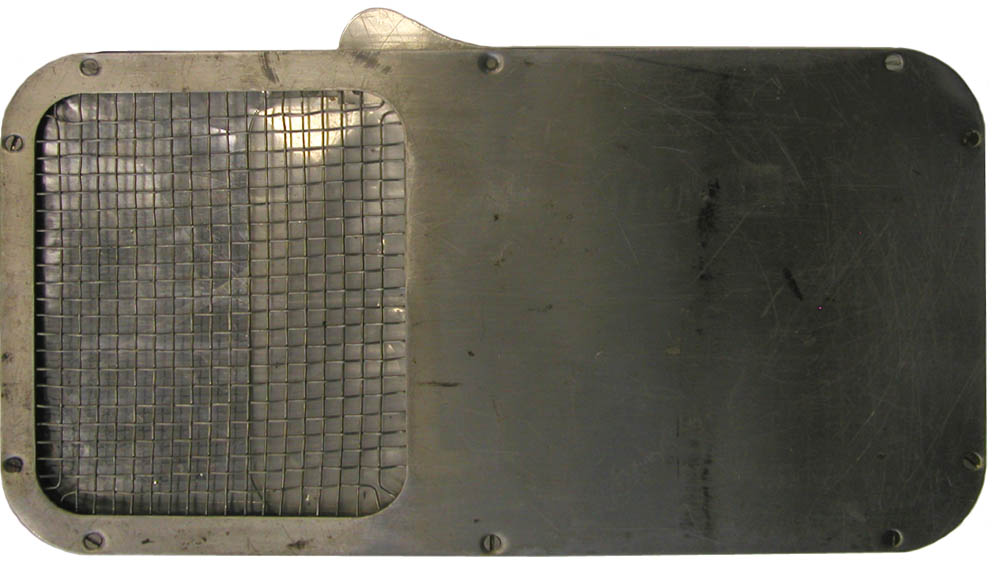

In the top photo, the handle to control the plastic beta shield is seen protruding from the upper left corner of the detector. In the photo (above right) showing the bottom of the meter, the aluminum beta shield is covering the lower portion of the window.

Chamber: Ion chamber
Range: 0-25, 0-100, 0-500, 0-2500 mR/hr (these correspond to 0-20 microamperes on the X1, X4, X20, and X100 ranges)
Size: 13" x 10 3/8" x 5 3/8"
Weight: 10 1/3 lbs
For technical details pertaining to the design of this instrument see Metallurgical Laboratory Project report Shonka, F.R. et al., "Zeus", A Portable Ionization Chamber, Nov. 1944.
Donated by Herbert Clark.
Reference
Campbell, D.C. Radiological Defense, Vol. IV, Armed Forces Special Weapons Project, 1950.
